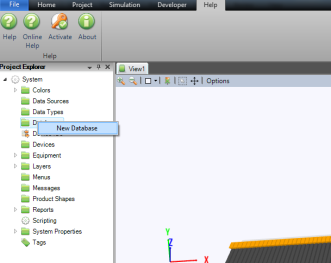
To create a new Database right click on Database and New Database

Once New Database is created move to user properties of Database and set the following:
Name: Name will be the database name.
DatabaseID: Database ID will be the database ID used for making connection.
Database Provider Type: It will be the provider installed on you machine for e.g SqlClient data Provider,Oledb Provider,ODP.NET.Managed Driver etc.
The combo box to select the provider is editable and if find the similar provider it will auto complete the text. User can enter free text so he can configure a project with a provider that is not available on this machine.
If user enter invalid text like "RDBMS". The 'Test Connection' button will tell him that the provider is not known.
Note: For creation of Oracle client you can install the Oracle Database Access Driver from
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/topics/dotnet/utilsoft-086879.html
Connection String: Connection string for the selected Database Provider Type. Sym3 will check every possible provider installed on the computer and will populate the "Database Provider Type" combo box accordingly.
To have examples of connection string for your provider, please visit this following web site:
https://www.connectionstrings.com/
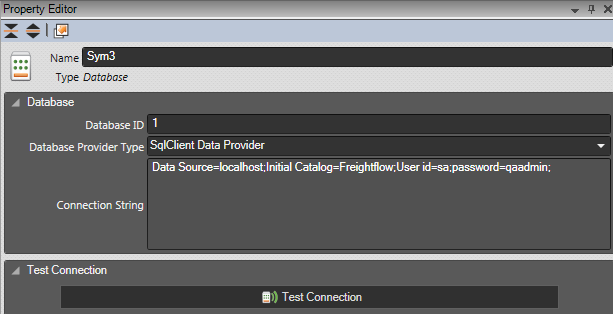
Sample connection string for SqlClient Data Provider:"Data Source=172.29.26.16;Initial Catalog=Sym3;User id=sa;password=sa;
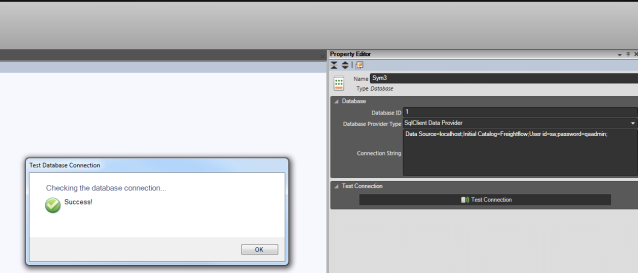
Once all of the above has been in place. Click on Test Connections to make sure connection with the database is successful.
Creation of Database using Macro:
Database can be created using a Macro show in example below:
Example:
var newEntity = Project.Databases.New()
newEntity.DatabaseID = 1; newEntity.DatabaseProviderType = "SqlClient Data Provider"; newEntity.ConnectionString = "Data Source=172.29.26.64;Initial Catalog=Sym3;User id=sa;password=sa;"; newEntity.Name = "Sym3DB";
Database Scripting
Once database is created it can be access in simulation script using the following:
GetDatabase
var arr = GetDatabases();
for (var i = 0; i < arr.length; ++i)
{
LogDebug("Database ID " + arr[i].DatabaseId);
LogDebug("Database Name " + arr[i].Name);
LogDebug("Database ConnectionString " + arr[i].ConnectionString);
LogDebug("Database DatabaseProviderName " + arr[i].DatabaseProviderName);
}
GetDatabaseByID(ID)
var a = GetDatabaseById(7);
LogDebug("Database ID " + a.DatabaseId);
LogDebug("Database Name " + a.Name);
LogDebug("Database ConnectionString " + a.ConnectionString);
LogDebug("Database DatabaseProviderName " + a.DatabaseProviderName);
GetDatabaseByName(Name)
var a = GetDatabaseByName("Sym3DB");
LogDebug("Database ID " + a.DatabaseId);
LogDebug("Database Name " + a.Name);
LogDebug("Database ConnectionString " + a.ConnectionString);
LogDebug("Database DatabaseProviderName " + a.DatabaseProviderName);
SetSQLCmdEx
var db1 = GetDatabaseById(1);
SetSQLCmdEx(db1, 1, "SELECT Datanumber,Location * FROM [AF_BCS_C].[dbo].[DatabaseConnection]", "callback");
1) Parameter 1: The connection to the database object. Usually we could configure the database object in the project and use GetDatabaseX function to get the object;
2) Parameter 2: The command id, which will be passed to the callback function to execute the command which is associated with the result;
3) Parameter 3: The SQL query string;
4) Parameter 4: The callback function (can be a string or function name)
function callback(id, result)
{
var selectData=result.split("\n");
for (var i=0;i< selectData.length;i++)
{
var fetchdata=selectData[i].split(",");
var datano=fetchdata[0];
var location=fetchdata[1];
}
}